New precipitation capabilities from the radar wind profilers
Submitter
Williams, Christopher R — University of Colorado Boulder
Area of research
Cloud Processes
Journal Reference
Science
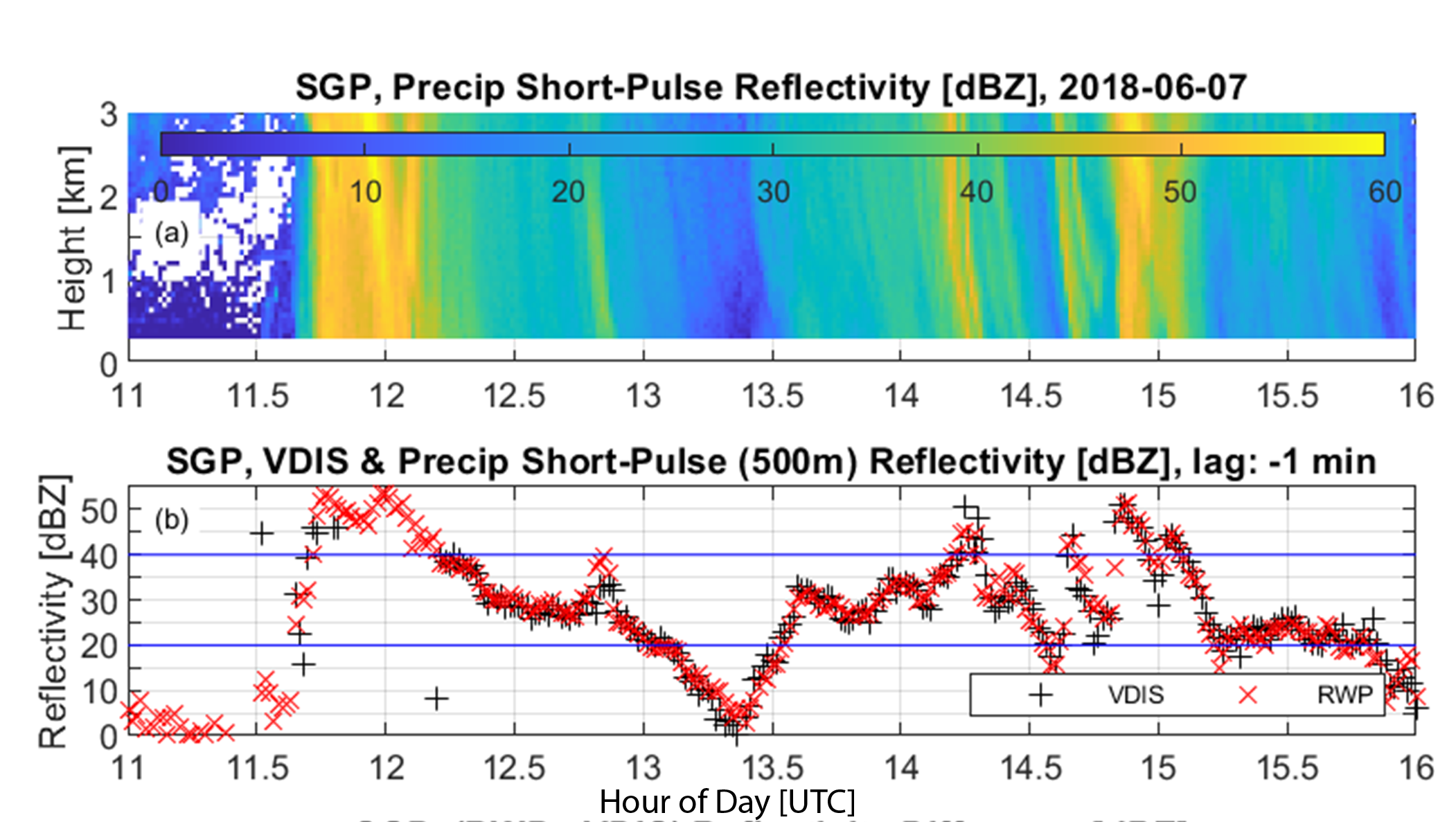
The radar reflectivity factor quantifies the intensity of precipitation and is needed to study microphysical processes and vertical structure of precipitation. This work developed software to estimate and calibrate the radar reflectivity factor from radar wind profiler (RWP) observations.
Impact
Prior to this ASR-funded data product project, end users needed to estimate and calibrate the RWP radar reflectivity factor themselves before performing any science with the RWP observations. Now, over 10 years of calibrated RWP radar reflectivity factor from the Southern Great Plains (SGP) ARM observatory are available for the community at the ARM Data Center and accessible via the ARM Discovery tool. Also, the new software was incorporated into the ARM infrastructure processing procedure so that ARM can produce calibrated RWP radar reflectivity factor products from multiple ARM sites.
Summary
RWPs were originally designed to estimate horizontal wind during clear-sky conditions. When it is raining, the original RWP signal-processing routines produce biased precipitation products unsuitable for ARM precipitation science. To overcome these issues, this project (1) developed new signal-processing routines that are valid for both clear-sky and rainy periods, (2) calibrated the radar reflectivity factor using collocated surface disdrometer observations, (3) uploaded over 10 years of calibrated RWP data to the ARM Data Center that are accessible through the ARM Data Discovery tool, and (4) provided the signal-processing code in Python to the ARM infrastructure so that ARM can perform this processing on multiple (and historical) RWP data sets.